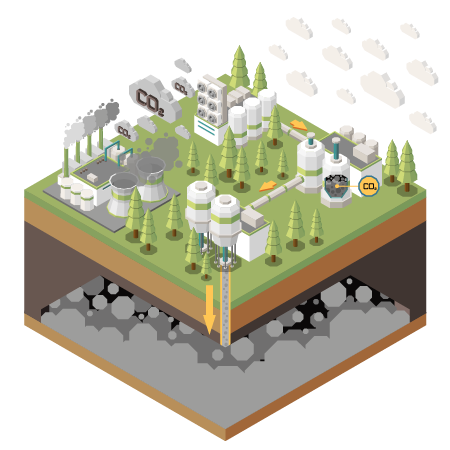
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is an innovative set of technologies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions by capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) at its source, utilizing it for industrial applications, or permanently storing it underground. These solutions are critical to achieving global climate goals and transitioning to a sustainable, low-carbon economy.
Benefits of CCUS
- Emission reduction: Captures up to 90% of CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power generation.
- Economic opportunities: Enables the development of new markets and industries around CO2 utilization.
- Energy transition support: Provides a pathway to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors like cement, steel, and chemical production.
- Climate goals: Plays a vital role in meeting the targets set by the Paris Agreement.
Challenges and Considerations
- High costs: The technologies are capital-intensive, requiring significant investments.
- Energy requirements: Carbon capture processes can consume substantial amounts of energy, potentially reducing overall efficiency.
- Storage risks: Long-term monitoring is needed to ensure the safe containment of CO2.
- Policy and regulation: Robust legal and regulatory frameworks are necessary to support CCUS deployment.
Current Trends and Future Prospects
- Global deployment: CCUS projects are operational in several countries, including the United States, Canada, Norway, and China.
- Technological advancements: Research is focused on improving capture efficiency, reducing costs, and developing novel utilization pathways.
- Policy support: Governments and international organizations are increasingly providing incentives and funding for CCUS initiatives.
- Integration with renewable energy: CCUS can complement renewable energy by addressing intermittency and decarbonizing industrial emissions.
