The sum of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) of any particular Human Activity is generally referred to as a Carbon Footprint.
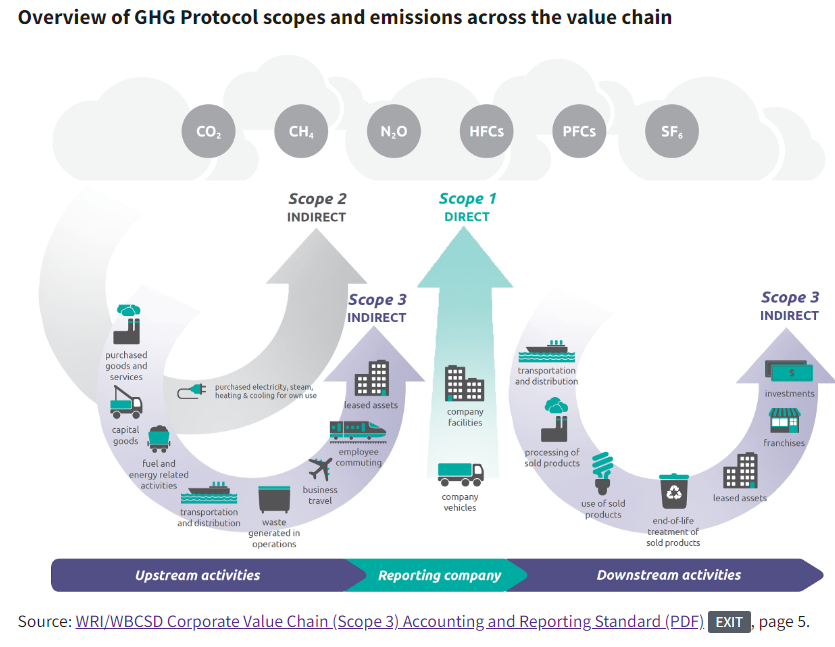
A CFP is a measure of the impacts of an activity on global warming by calculating the greenhouse gas emissions of these activities, usually stated as a ‘CO2e’, or carbon dioxide equivalent. This is done to show all key greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide) expressed as a common unit, allowing easy comparison across organisations, industries and countries. What are carbon footprint scopes? Emissions are defined under three categories, or ‘Scopes’ – Scope 1, 2 and 3.
A Carbon Footprint (CFP) may be attributable to an Individual Citizen, an Organisation of Citizens such as a School or University, or a Business Related activity.
Taken all together, for an Individual State such as the United Kingdom, the sum of all such CFPs is termed a Nationally Determined Contribution (NDA).
A CFP is calculated through the evaluation of the different GHG ‘Scopes’. These are Scope 1 (direct emissions ), Scope 2 (indirect emissions), and Scope 3 (supply chain emissions). More detailed information may be found here.